Minimum wages are the lowest wages that an employer is legally required to pay to their workers. This ensures that workers receive a fair payment for their labour. In India, the concept of minimum wages is regulated by the Minimum Wages Act of 1948. This law aims to prevent the exploitation of workers by ensuring they receive wages that meet their basic needs.
Key Points About Minimum Wages in India
- Legislation: The Minimum Wages Act, 1948, empowers both the Central and State governments to fix and revise minimum wages for various categories of employment.
- Coverage: The Act covers a wide range of industries and occupations, ensuring that workers in different sectors receive fair wages.
- Frequency of Revision: Minimum wages are typically revised every five years. However, adjustments can be made more frequently to account for changes in the cost of living.
- Components: Minimum wages can include:
- Basic Wage: The core amount paid to the worker.
- Dearness Allowance (DA): An allowance to counteract inflation and the rising cost of living.
Categories of Workers
In India, workers are classified into three categories based on their skill levels:
- Unskilled Workers:
- These workers perform tasks that require no special skills or training.
- Examples: Cleaners, helpers, loaders, and agricultural labourers.
- Semi-skilled Workers:
- These workers have some basic skills or training and perform tasks that require a moderate level of skill.
- Examples: Drivers, machine operators, and clerks.
- Skilled Workers:
- These workers have specialized skills and training and perform tasks that require a high level of competence and expertise.
- Examples: Electricians, plumbers, carpenters, and technicians.
Revision of Minimum Wages
- Frequency of Revision:
- The minimum wages in India are revised twice a year to adjust for changes in the cost of living and inflation.
- Revisions are typically done in the months of January and July.
- Duration of Revision:
- Each revision is effective for a period of six months.
Minimum Wage Rates
The minimum wage rates vary based on several factors:
- State: Each state in India can set its own minimum wage rates, which can differ from the national minimum wage.
- Industry: Different industries may have different minimum wage rates.
- Location: Wages can vary within a state based on whether the work is performed in urban or rural areas.
For example, the minimum wage for an unskilled worker in a rural area might be lower than that for a similar worker in an urban area, reflecting differences in the cost of living.
Importance of Minimum Wages
- Worker Protection: Ensures that workers earn enough to meet their basic needs, such as food, shelter, and clothing.
- Poverty Reduction: Helps in reducing poverty by providing a basic standard of living for workers.
- Economic Stability: Contributes to economic stability by increasing the purchasing power of workers, leading to higher consumption and demand for goods and services.
Compliance
- Employers are legally bound to pay their workers at least the minimum wage as set by the government.
- Non-compliance can lead to legal consequences, including fines and penalties.
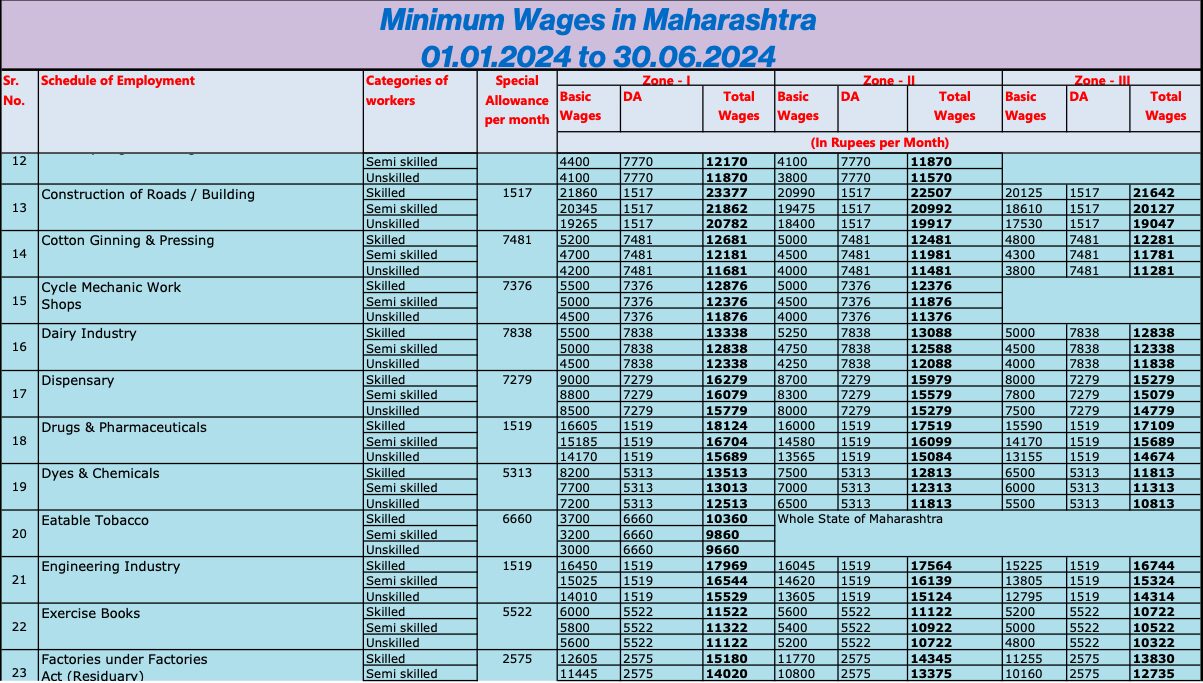
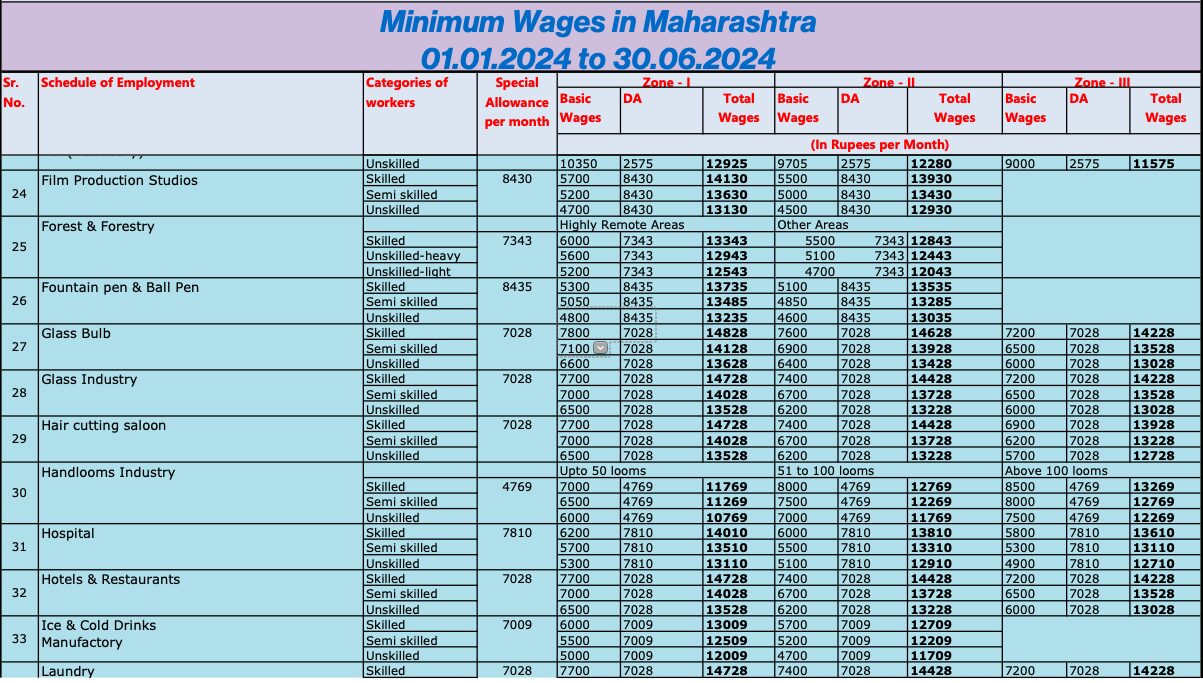
Below are minimum wages as per latest notification effective from 1st July 2024 to 31st December 2024 for your reference.





India Business Head
Mrs. Dipali Phadke is a qualified Chartered Accountant with more than 20+ years of experience in the field of Accounting, Taxation and Payroll. She is the backbone of Company’s Operations and heads India Business at Finsmart Accounting










